一、概念
¶1、同步和异步
¶同步:
用户线程发起I/O请求后需要等待或者轮询内核I/O操作完成后才能继续执行
¶异步:
用户线程发起I/O请求后仍需要继续执行,当内核I/O操作完成后会通知用户线程,或者调用用户线程注册的回调函数
¶2、阻塞和非阻塞
讨论的是参与通信双方的工作机制,是否需要互相等待对方的执行
¶阻塞:
在通信过程中,
一方在处理通信,
另一方要等待对方执行并返回信息不能去做其他无关的事
¶非阻塞:
在通信过程中,
一方在处理通信,
另一方可以不用等待执行并返回信息而可以去做其他无关的事 直到对方处理通信完成 再在适合的时候继续处理通信过程
二、BIO (同步阻塞)
¶代码示例
服务端业务代码
1 | import javax.script.ScriptEngine; |
服务端代码
1 | import java.io.IOException; |
客户端代码
1 | import java.io.BufferedReader; |
测试
1 | import java.io.IOException; |
¶问题
同步阻塞式I/O创建的Server
¶结构图
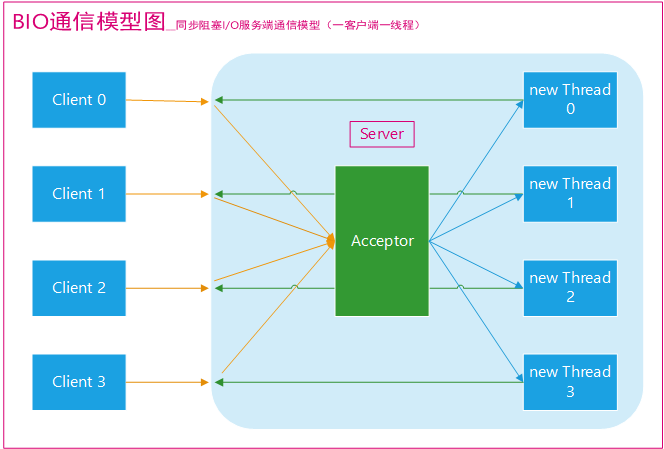
¶1、BIO主要的问题在于每当有一个新的客户端请求接入时,服务端必须创建一个新的线程来处理这条链路,在需要满足高性能、高并发的场景是没法应用的(大量创建新的线程会严重影响服务器性能,甚至罢工)
¶1、限制了线程数量,如果发生大量并发请求,超过最大数量的线程就只能等待,直到线程池中的有空闲的线程可以被复用。而对Socket的输入流进行读取时,会一直阻塞
所以在读取数据较慢时(比如数据量大、网络传输慢等),大量并发的情况下,其他接入的消息,只能一直等待,这就是最大的弊端。而NIO,就能解决这个难题
三、NIO
¶代码示例
服务端代码
1 | import javax.script.ScriptEngine; |
客户端代码
1 | import java.io.IOException; |
测试代码
1 | import java.util.Random; |
¶nio 结构
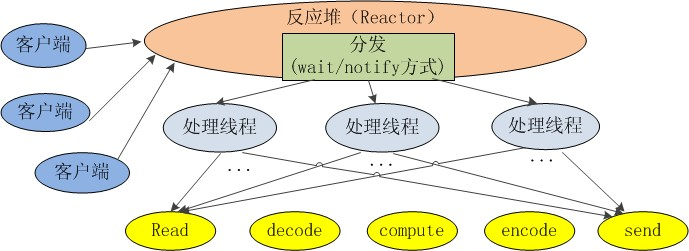
¶服务端
- 打开ServerSocketChannel,监听客户端连接
- 绑定监听端口,设置连接为非阻塞模式
- 创建Reactor线程,创建多路复用器并启动线程
- 将ServerSocketChannel注册到Reactor线程中的Selector上,监听ACCEPT事件
- Selector轮询准备就绪的key
- Selector监听到新的客户端接入,处理新的接入请求,完成TCP三次握手,建立链路
¶客户端
- 设置客户端链路为非阻塞模式
- 将新接入的客户端连接注册到Reactor线程的Selector上,监听读操作,读取客户端发送的网络消息
- 异步读取客户端消息到缓冲区
- 对Buffer编解码,处理半包消息,将解码成功的消息封装成Task
- 将应答消息编码为Buffer,调用SocketChannel的write将消息异步发送给客户端
¶Selector(多路复用器|选择某个通道器)
选择器类管理着一个被注册的通道集合的信息和它们的就绪状态。
通道是和选择器一起被注册的,并且使用选择器来更新通道的就绪状态,
当这么做的时候,可以选择将被激发的线程挂起直到有就绪的通道。
使用Selector的好处在于: 使用更少的线程来就可以来处理通道了, 相比使用多个线程,避免了线程上下文切换带来的开销。
¶SelectionKey
表示了一个特定的通道对象和一个特定的选择器对象之间的注册关系。
key.attachment(); //返回SelectionKey的attachment,attachment可以在注册channel的时候指定。
key.channel(); // 返回该SelectionKey对应的channel。
key.selector(); // 返回该SelectionKey对应的Selector。
key.interestOps(); //返回代表需要Selector监控的IO操作的bit mask
key.readyOps(); // 返回一个bit mask,代表在相应channel上可以进行的IO操作。
| 事件名 | 对应值 |
|---|---|
| 服务端接收客户端连接事件 | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT(16) |
| 客户端连接服务端事件 | SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT(8) |
| 读事件 | SelectionKey.OP_READ(1) |
| 写事件 | SelectionKey.OP_WRITE(4) |
¶buffer(解决bio中数据不可重复读的问题)
存储基本类型数组数据:ByteBuffer、CharBuffer、FloatBuffer、ShortBuffer、StringCharBuffer等等
这些方法中大部分是对mark、position、limit、capacity的操作。
对于数组来说,需要以下一些重要元素,比如数组大小(capacity)
此时如果是对数组的读取操作时,需要表明当前读到了哪个位置(position),总共可以读到哪个位置(limit),也就是当前数组中有几个元素。
此时如果是写操作,那么需要知道现在写到了哪个位置(position),最大可以写到哪个位置(limit)
最后为了实现可重复读,产生一个备忘位置,即标记(mark)。
源码(只截取部分):
1 | public abstract class Buffer { |
直接缓冲区与非直接缓冲区(ByteBuffer):
- 非直接缓冲区:
优点:在虚拟机内存中创建,易回收
缺点:但占用虚拟机内存开销,处理中有复制过程。 - 直接缓冲区:
优点:在虚拟机内存外,开辟的内存,IO操作直接进行,没有再次复制
缺点:创建和销毁开销大,没有管理权(基于系统的物理内存没有分代回收机制)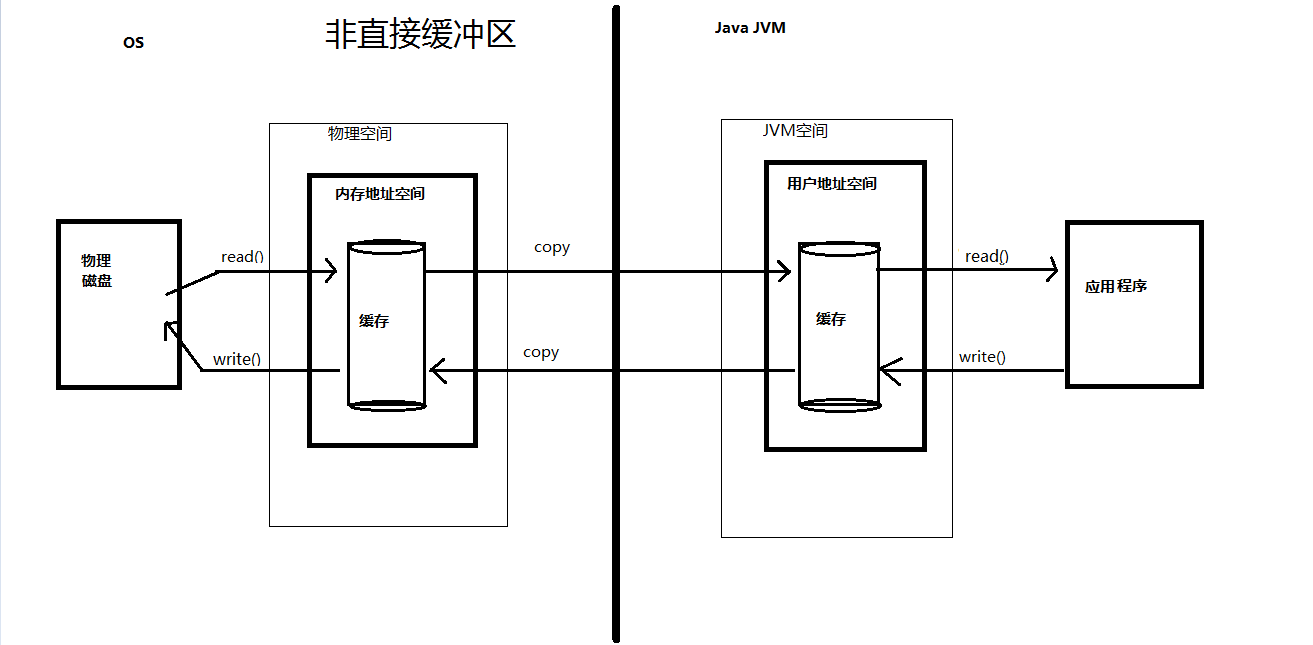
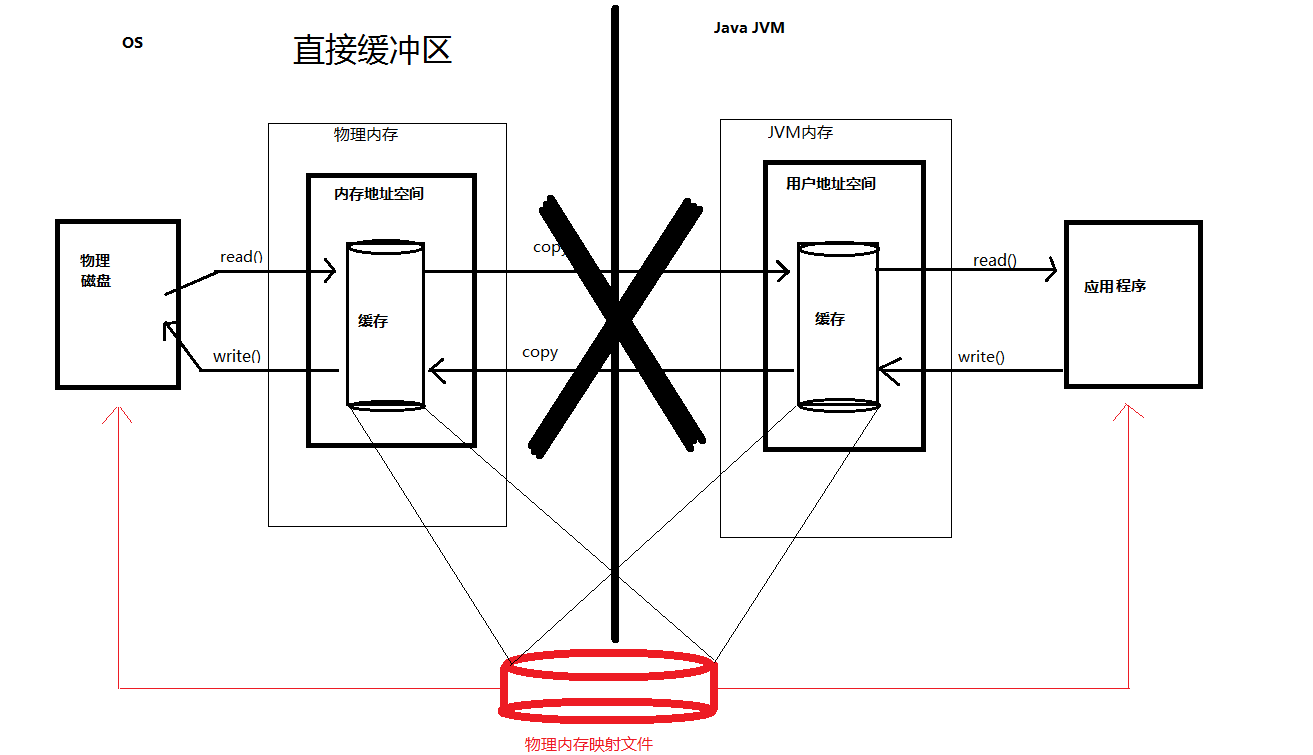
用通俗的话讲就是,比如你是个小组长(jvm堆内存),你管理者你底下的人,
但是你的领导(内核[物理空间])要知道你的情况,你需要把你的组内的情况汇报给他(复制),而他自己本身只知道你的情况,你下面人的情况他是不了解的也是不关心的,相当于他把这块区域分配给你,至于你要干什么,他是不管的
JVM创建一个缓冲区的时候,实际上做了如下几件事:
- JVM确保Heap区域内的空间足够,如果不够则使用触发GC在内的方法获得空间;
- 获得空间之后会找一组堆内的连续地址分配数组, 这里需要注意的是,在物理内存上,这些字节是不一定连续的;
- 对于不涉及到IO的操作,这样的处理没有任何问题,但是当进行IO操作的时候就会出现一点性能问题.
所有的IO操作都需要操作系统进入内核态才行,而JVM进程属于用户态进程, 当JVM需要把一个缓冲区写到某个Channel或Socket的时候,需要切换到内核态.
而内核态由于并不知道JVM里面这个缓冲区存储在物理内存的什么地址,并且这些物理地址并不一定是连续的(或者说不一定是IO操作需要的块结构),
所以在切换之前JVM需要把缓冲区复制到物理内存一块连续的内存上, 然后由内核去读取这块物理内存,整合成连续的、分块的内存.
三、AIO
¶代码示例:
服务端代码
1 | import javax.script.ScriptEngine; |
客户端代码
1 | import java.io.IOException; |
测试代码
1 | import java.util.Random; |
四、总结
¶同步和异步
我认为的网络层面io的同步和异步描述的是一种消息通知的机制,主动等待消息返回还是被动接受消息
同步io:指的是调用方通过主动等待获取调用返回的结果来获取消息通知。
异步io:指的是被调用方通过某种方式(如,回调函数)来通知调用方获取消息。
¶阻塞和非阻塞
NIO、AIO为什么被称为非阻塞?
- BIO在发起读请求以后,会一直等待,一直到拿到结果
- NIO在发起读请求以后,不会立即拿到结果
- AIO通过回调方法,被动的接受
¶BIO(blocking IO):
同步阻塞式IO 面向流 操作字节或字符 单向传输数据
¶NIO(non blocking IO):
同步非阻塞式IO 面向通道 操作缓冲区 双向传输数据
¶AIO(async IO):
同步非阻塞式IO 大量使用回调函数 异步处理通信过程 异步的双向传输数据
